Truyền động xích
Thông thường, công suất được truyền bởi một xích con lăn, được gọi là xích truyền động. Hoặc là xích truyền động, truyền qua một bánh răng xích, với các răng của bánh răng chia lưới với các lỗ trên các liên kết của xích. Bánh răng được quay, và điều này kéo dây xích đưa lực cơ học vào hệ thống.
Các dây xích công nghiệp được tạo thành từ một số liên kết cứng được gắn với nhau bằng các khớp chốt để cung cấp sự linh hoạt cần thiết để bọc các bánh xe dẫn động và dẫn động.
Các bánh xe này có răng định hình đặc biệt và phù hợp với phần lõm tương ứng trong liên kết xích. Bánh xe có răng được gọi là bánh xe xích. Do đó, nhông và xích được hạn chế chuyển động cùng nhau mà không bị trượt và đảm bảo tỷ lệ vận tốc chính xác.
Xích chủ yếu được sử dụng để truyền tốc độ và công suất từ trục này sang trục khác khi khoảng cách tâm giữa các trục của chúng ngắn như xe đạp, xe máy, máy móc nông nghiệp, băng tải, máy cán, xe lu, v.v.
Xích cũng có thể được sử dụng cho khoảng cách trung tâm dài. Xích được sử dụng cho vận tốc lên đến 25m/s và công suất lên đến 110 kW. Trong một số trường hợp, cũng có thể truyền công suất lớn.
Các xích cũng được sử dụng trong băng tải thường là các xích khối và bao gồm các khối rắn hoặc nhiều lớp được kết nối bằng các tấm bên và các chốt. Các khối ăn khớp với các răng trên bánh xích. Tùy thuộc vào vật liệu được di chuyển, xô, móc hoặc các thiết bị khác được kết nối với các khối.

Thuật Ngữ Của Truyền Động Xích
• Bước xích: Là khoảng cách giữa tâm bản lề của một liên kết và tâm bản lề tương ứng của một liên kết liền kề. Nó thường được ký hiệu là p.
- Đường kính vòng tròn cao độ của đĩa xích: Đây là đường kính của vòng tròn mà tâm bản lề của xích nằm trên đó khi xích được quấn bằng một quả bóng. Các tâm bản lề của chuỗi và đường tròn được vẽ qua các tâm này được gọi là đường tròn cao độ và đường kính của nó được gọi là đường kính vòng tròn góc.
Sau đây là ba loại xích truyền động:
• Xích kéo và cầu.
• Xích băng tải.
• Xích truyền lực.
Xích kèo và cấu
Palăng là một thiết bị để nâng hoặc hạ tải bằng cách sử dụng tang trống hoặc bánh xe nâng có quấn dây hoặc xích. Nó có thể được vận hành bằng tay, bằng điện hoặc bằng khí nén và có thể sử dụng dây xích, sợi hoặc dây thừng làm phương tiện nâng.
Dạng được biết đến nhiều nhất là thang máy, vận chuyển được nâng lên và hạ xuống bằng một cơ cấu nâng. Hầu hết, các vận thăng được gắn vào tải của chúng bằng một móc nâng.
Những dây xích này được sử dụng để cầu và hoạt động với vận tốc tối đa là 0,25 m/s. Xích cầu thường có hai loại sau:
• Xích có các mắt xích hình bầu dục: Loại mắt xích này có hình bầu dục. Mỗi mối nối liên kết được hàn. Các đĩa xích được sử dụng cho loại xích này có các cơ quan tiếp nhận để có được liên kết. Những loại xích này chỉ được sử dụng ở tốc độ thấp như pa lăng xích và neo trong các hoạt động hàng hải.
• Xích có mắt xích hình vuông: Các mắt xích của loại dây xích này có dạng hình vuông. Những chuỗi như vậy được sử dụng trong vận thăng, cần trục, tàu hút bùn. Chi phí sản xuất của loại xích này thấp hơn loại xích có mắt xích hình bầu dục, nhưng ở những loại xích này, quá tải rất dễ bị gấp khúc.
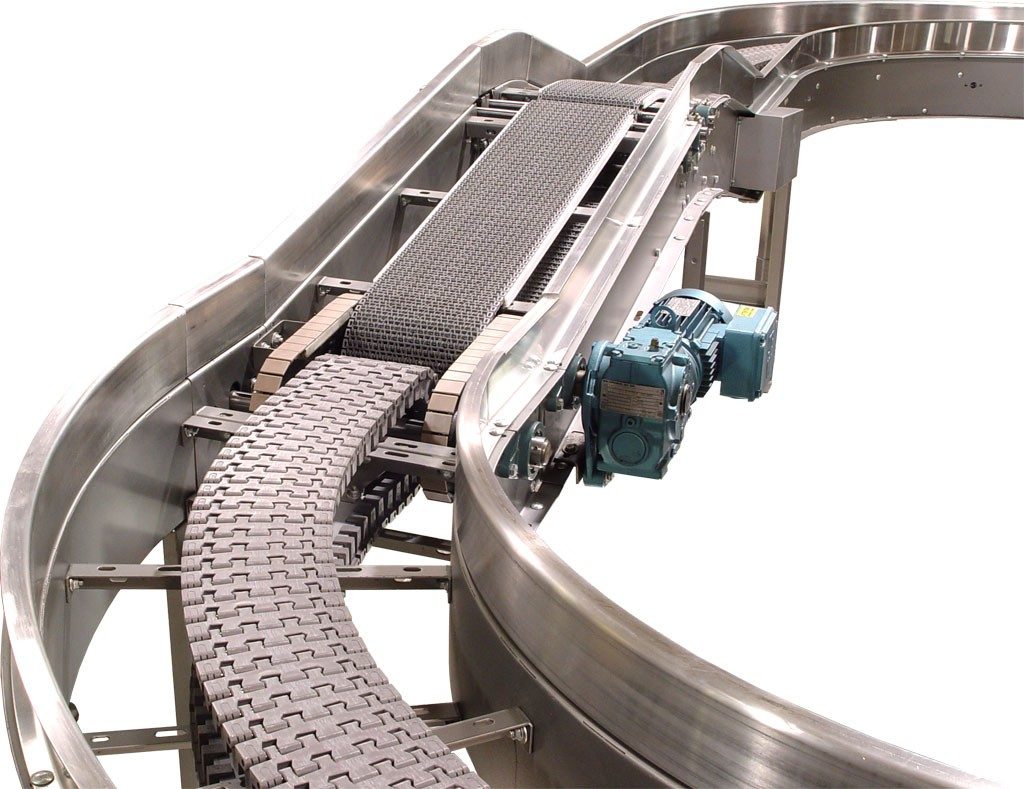
Xích băng tải
Là một loại xích được phát triển đặc biệt cho các hệ thống băng tải xích. Nó bao gồm một loạt các ổ trượt được giữ với nhau bằng các tấm kết nối. Mỗi ổ trục bao gồm một chốt và một ống lót mà trên đó con lăn xích quay.
Những dây xích này được sử dụng để liên tục nâng và chuyển tải vật liệu với tốc độ lên đến 2 m / s. Có hai loại dây chuyền băng tải:
• Xích loại có thể tháo rời hoặc loại khớp móc: Loại xích tải này được sử dụng trong băng tải mà chiều dài giữa các bộ truyền lực ngắn.
• Xích kiểu khớp kín: Loại xích này bao gồm một nòng và mắt xích và được đúc thành một khối duy nhất, sau đó dây xích được nhiệt luyện để mang lại độ bền cao.
Xích băng tải thường được làm bằng gang dễ uốn. Các chuỗi này không có đặc tính chạy trơn tru. Xích băng tải hoạt động với tốc độ chậm khoảng 0,8 - 3m/s.

Xích Dùng Trong Ngành Điện
Xích truyền lực được sử dụng để truyền cơ năng khi khoảng cách giữa các tâm trục ngắn. Các dây chuyền này có các quy định để bôi trơn hiệu quả. Xích được dùng trong ngành điện có ba loại sau đây.
1. Xích khối hoặc xích đúc.
2. Xích con lăn đúc.
3. Xích giảm tiếng ồn (Silent chain).
1) Xích khối hoặc xích đúc
Loại xích này được sử dụng trong giai đoạn phát triển ban đầu trong lĩnh vực truyền tải điện. Nó gây ra tiếng ồn khi cọ xát giữa các răng và liên kết khi đĩa xích ở gần hoặc ra khỏi các răng. Các loại xích này được sử dụng ở một mức độ nào đó với tốc độ nhỏ như xích băng tải.
2) Xích Con Lăn Đúc
Xích con lăn ống lót bao gồm tấm bên ngoài hoặc tấm liên kết chốt, tấm bên trong hoặc tấm liên kết con lăn, chốt, ống lót và con lăn. Một chốt đi qua ống lót được giữ chặt trong lỗ của con lăn giữa hai mặt của xích.
Các con lăn tự do quay trên ống lót để bảo vệ răng bánh xích khỏi bị mài mòn. Ghim, ống lót và con lăn được làm bằng thép hợp kim.
Xích con lăn dạng ống cực kỳ chắc chắn và sản xuất đơn giản. Nó phục vụ tốt trong điều kiện khắc nghiệt. Có một tiếng ồn nhỏ với xích này do tác động của các con lăn lên các răng của bánh xích. Xích này có thể được sử dụng ở những nơi có dầu bôi trơn nhẹ.
Khi một trong những xích này trở nên hơi dài ra do mòn và giãn của các bộ phận, thì đĩa xích kéo dài sẽ lớn hơn bước răng của bánh xe. Các con lăn ăn khớp không đều trong các hốc của bánh xe. Kết quả là tổng trọng lượng rơi vào một răng hoặc một vài răng. Việc kéo căng các bộ phận làm tăng độ mài mòn của bề mặt con lăn và các răng của bánh xích.
Xích con lăn được tiêu chuẩn hóa và sản xuất trên cơ sở cao độ. Các chuỗi này có sẵn trong chuỗi con lăn một hàng hoặc nhiều hàng, chẳng hạn như đơn giản, song công hoặc một sợi ba.
3) Xích giảm tiếng ồn (Silent chain)
Xích giảm tiếng ồn hay còn gọi là chuỗi răng ngược. Nó được thiết kế để loại bỏ các tác động xấu do kéo căng và tạo ra việc đi bộ không ồn ào. Khi xích bị kéo căng và bước răng của xích tăng lên, các mắt xích sẽ bám trên các răng của bánh xích theo bán kính tăng lên một chút.
Điều này tự động sửa những thay đổi nhỏ về cao độ. Không có sự trượt tương đối giữa các răng của xích răng ngược và bánh xích. Khi được bôi trơn đúng cách, xích này sẽ hoạt động bền bỉ và chạy rất trơn tru và yên tĩnh.
Ưu Điểm Của Truyền Động Xích
Đây là một số ưu điểm của bộ truyền động xích so với bộ truyền động đai và bánh răng.
• Chúng có thể được sử dụng cho cả khoảng cách dài và ngắn.
• Một số trục và được dẫn động từ một chuỗi duy nhất.
• Chúng nhỏ gọn và có kích thước tổng thể nhỏ.
• Ngay cả trong các nguy cơ hỏa hoạn, nó không phải đối mặt với bất kỳ vấn đề xấu.
• Nhiệt độ và điều kiện môi trường không ảnh hưởng đến hoạt động của chúng.
• Lực căng ban đầu không cần thiết trong bộ truyền động xích.
• Chúng có hiệu suất rất cao (lên đến 96%).
• Không bị trượt và dão trong quá trình truyền lực, đảm bảo tỷ số vận tốc hoàn hảo.
• Bộ truyền động xích dễ dàng lắp đặt.
• Bộ truyền động xích có chi phí bảo trì thấp.
• Chúng có thể chịu được các điều kiện mài mòn.
• Chúng có thể hoạt động trong điều kiện ẩm ướt.
Nhược Điểm Của Truyền Động Xích
• Hệ thống truyền động xích không thể được sử dụng khi trượt là yêu cầu của hệ thống.
• Nó yêu cầu căn chỉnh chính xác so với truyền động đai.
• Sản lượng của bộ truyền động xích cao hơn bộ truyền động đai.
• Bộ truyền động xích yêu cầu bôi trơn thường xuyên.
• khả năng tải ít hơn so với truyền động bánh răng.
• Bộ truyền động xích thông thường bị rung do hiệu ứng dây cung.
• Chúng không thích hợp cho các trục không song song.
• Chúng không thể được sử dụng khi cần chuyển động chính xác.
• Bộ truyền động xích cần lắp chính xác và cẩn thận.
• Chúng yêu cầu các điều chỉnh cho độ chùng như thiết bị căng.
Ứng Dụng Của Truyền Động Xích
Truyền động xích được sử dụng trong nhiều loại ứng dụng công nghiệp, chẳng hạn như:
• Thiết bị được sử dụng rộng rãi để truyền công suất trong đó các trục được tách ra ở khoảng cách lớn hơn khoảng cách mà các bánh răng được sử dụng trong thực tế.
• Làm giàn và di chuyển vật liệu nặng.
• Vận hành xe nâng thủy lực.
• Tăng hoặc giảm tốc độ đầu ra của trình điều khiển bằng cách thay đổi tỷ số truyền giữa trình điều khiển và đĩa xích được dẫn động.
• Palăng trên cao.
• Vận hành băng tải.
• Truyền động xích được sử dụng trong một số ngành công nghiệp cho một số mục đích như công nghiệp vận tải, máy móc nông nghiệp, thiết bị xử lý vật liệu, xây dựng tòa nhà.