1. Definition and characteristics of engineering plastics
Basically, plastic is a material with outstanding thermoplasticity, so it has the characteristic of very weak heat resistance. However, starting in the 1930s, plastics with excellent heat resistance and durability were developed one after another, and these plastics could be used for industrial purposes. Such plastics (synthetic plastics) are distinguished from regular civil plastics, and are called plastics used in engineering (technical plastics for short). Engineering plastics are lighter than metals so they are easier to mass produce. Therefore, it is used as a material that hits the intermediate segment between conventional plastics and metals to reduce weight and reduce costs.
Engineering plastics do not have a clear definition, but it can be simply understood that engineering plastics are plastics with long-term heat resistance of 100 ° C and tensile strength of 40Mpa or more.
2. Classify engineering plastics according to molecular structure
Engineering plastics are classified according to molecular structure and application.
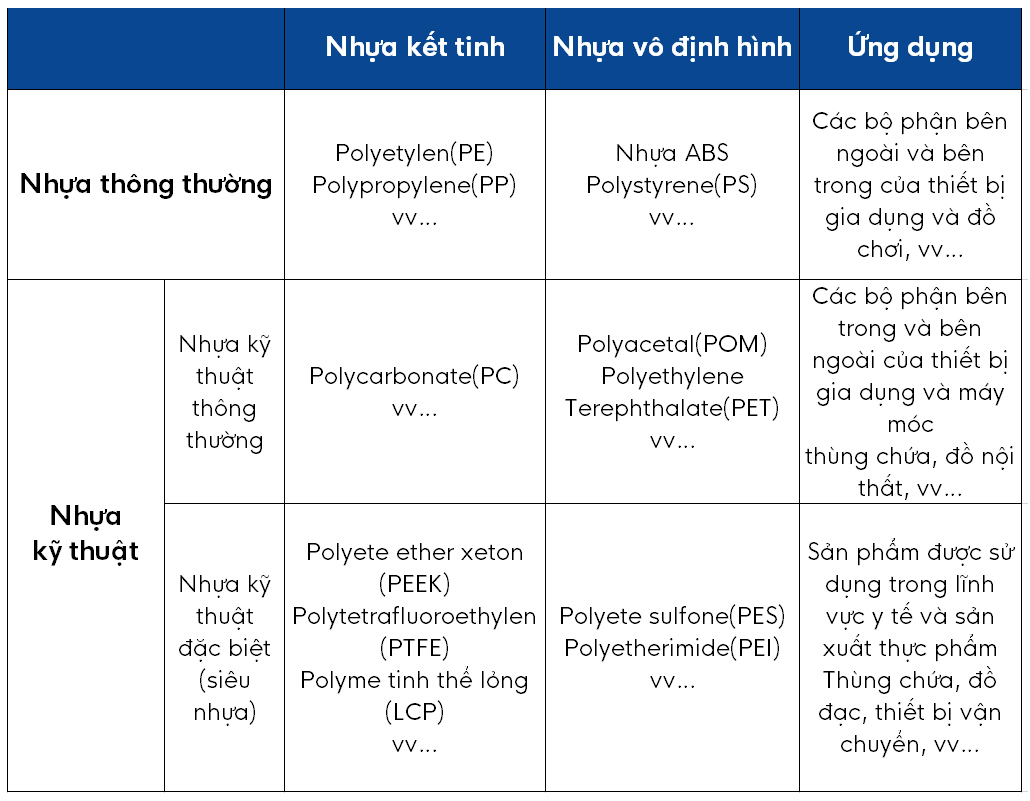
There are two types of plastics classified by molecular structure: amorphous plastics and crystalline plastics.
Amorphous engineering plastics are characterized by their transparency, such as polycarbonate (PC).
On the other hand, crystalline engineering plastics include polyacetal (POM) and polyethylene terephthalate (PET).
3. Classification of engineering plastics according to application
Engineering plastics are divided into normal engineering plastics and special engineering plastics (super engineering plastics) depending on the purpose of use.
Common engineering plastics include polycarbonate (PC), polyacetal (POM) and polyethylene terephthalate (PET), which are introduced in the classification according to molecular structure. They are engineering plastics commonly used in daily life.
Special engineering plastics (super engineering plastics) are one of the highest performance engineering plastics. Not only is it highly heat resistant and durable, but it also has features such as flame retardant and solvent resistance. For special engineering plastics, there is no clear definition, but one of the criteria is to have a heat resistance of 150°C or more.
4. Application of engineering plastics
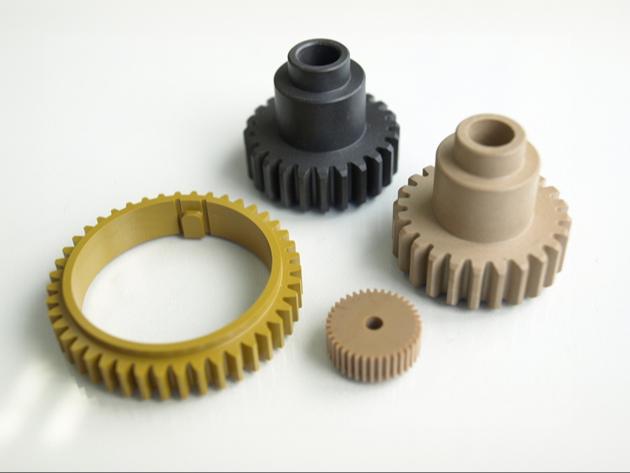
There are many types of engineering plastics, and they are used in many different applications. They are also used for mechanical parts such as plastic gears and car headlights, and they are also widely used for electrical and electronic parts. In addition, it is often used as a container for chemicals and liquids that you will often encounter in everyday life. It is also used for daily necessities such as photo frames and products such as bathtubs.

5. Advantages - Disadvantages of engineering plastics
As mentioned above, engineering plastics have many advantages but also weaknesses.
5.1 Advantages
Light
Easy to mass produce
Excellent heat resistance
Durable
Because engineering plastics are also plastics, they are light and easy to mass-produce in the same shape by injection molding, molding just like regular plastics. In addition, engineering plastics have superior heat and force resistance compared to conventional plastics, so they are easy to use for industrial purposes.
5.2 Disadvantages
Input materials are quite expensive.
Inferior to metal in terms of durability and heat resistance.
Some plastics are susceptible to aging from UV rays, oil and water.
For most types of plastic, it can be said that the price of input materials is a bit more expensive than steel. Furthermore, engineering plastics are more expensive than regular plastics. Although there are high-strength engineering plastics, their durability is still less than that of metals, so care must be taken when using them as load-bearing parts.
Furthermore, depending on the type, attention must be paid to dimensional changes due to spoilage and hydrolysis.
6. Processing and surface treatment methods commonly used for engineering plastics
Engineering plastics can be processed and processed by many different methods, the following are typical methods.
Molding - injection molding
Engineering plastics are often injection molded. The basic manufacturing method is the same as for conventional plastics, but more attention is needed than with conventional plastics, such as mold wear rate and molding temperature.
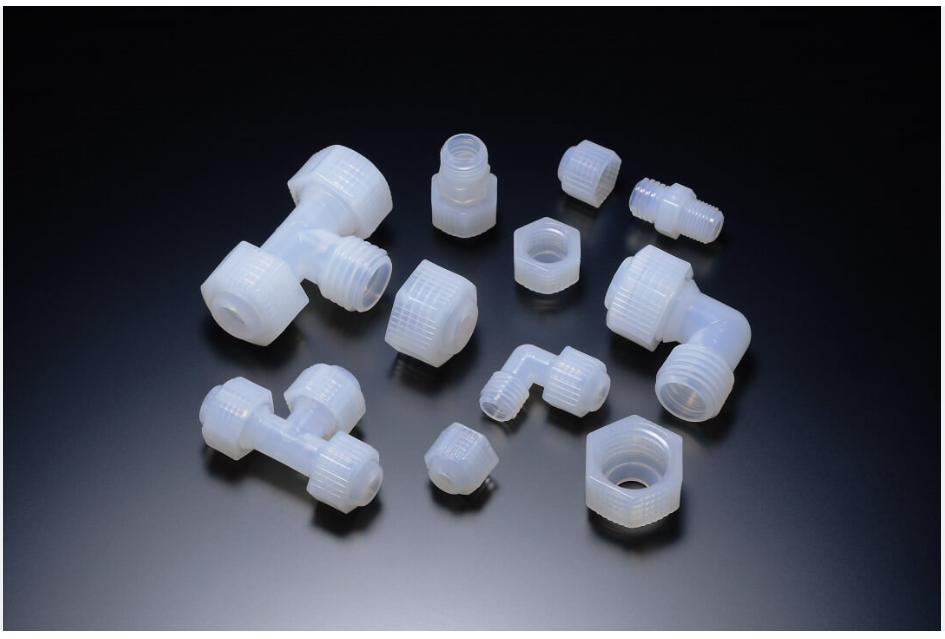

Machining and cutting
In some cases, engineering plastics are processed in the same way as regular plastics. And in some cases, shapes are created by machining from an original plastic blank when a mold is not available. In addition, machining processes such as hole drilling and gear cutting are also performed on engineering plastics.

Coating
Many types of engineering plastics are used for coating the exterior and buttons of electrical equipment, and there are many cases for decorative coating of products.
7. The most popular types of engineering plastics today
Polycarbonate (PC)
Polycarbonate, also known as polycarbonate, is a type of plastic with high transparency and excellent impact resistance. Therefore, it is widely used for covering materials and optical parts that require transparency. On the other hand, it is not resistant to harsh chemicals.
Polyamide (PA) (Nylon)
Polyamide is an engineering plastic also known as nylon. Because of its high mechanical strength and excellent wear resistance, it is used for machine parts such as gears and bearings. On the other hand, it is highly hygroscopic and therefore its size changes in humid environments.
Polyacetal (POM)
Polyacetal is an engineering plastic with high abrasion resistance and smooth surface, called Pom for short. Blog wrote a separate article about POM. You can read more details in the article at POM plastic. It is characterized by a silky and smooth feel, and has excellent sliding and abrasion resistance. It is commonly used as a material for machinery parts such as gears, bearings, and plastic springs. It has an opaque appearance and is essentially milky white in color.
Modified polyphenylene ether (m-PPE)
Modified polyphenylene ether is characterized by excellent mechanical strength and light weight. Therefore, it is also used for the housing of electrical devices. The downside is that it is weak against chemicals such as solvents.
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT)
Polybutylene terephthalate is characterized by high electrical insulating properties. It also has good sliding properties and a smooth surface. Therefore, it is used for electrical equipment parts and automobile electrical equipment parts. On the other hand, it also has the characteristic of being easily degraded by hydrolysis.
8. Other types of engineering plastics are quite popular for use
The following three types do not belong to the above 5 types, but are technical plastics that we often see in everyday life.
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET)
Polyethylene terephthalate is well known as a material for producing PET plastic bottles. It has the characteristics of being light and durable. It is commonly used as a fiber reinforced plastic by including glass fibers and carbon fibers.
Polyphenylene sulfide (PPS)
Polyphenylene sulfide is known as PPS. Generally, it is filled with fiberglass or carbon fiber. It has excellent heat resistance and very high mechanical strength. In addition, it also has the characteristic of being difficult to burn, so it is widely used in environments prone to explosion or high temperatures.
Polyetheretherketone (PEEK)
Polyetheretherketone must be called the pinnacle of engineering plastics or super engineering plastics. They are a typical super engineering plastic. In addition to being able to withstand high temperatures of 240°C and above, it also has extremely high mechanical strength and has very good impact resistance and chemical resistance. In addition, it has the characteristic of not causing hydrolysis even under high temperature steam. Of course the price will be more expensive than other types of plastic.